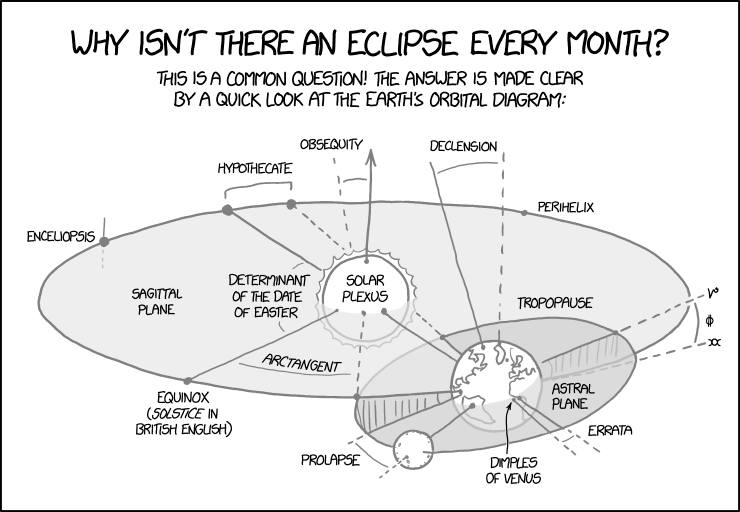
1878: Earth Orbital Diagram
| Earth Orbital Diagram |
 Title text: You shouldn't look directly at a partial eclipse because of the damage that can be caused by improperly aligning the solar-lunar orbital plane with the orbital bones around your eye. |
Explanation
| This is one of 60 incomplete explanations: Created by a BOT - Please change this comment when editing this page. Do NOT delete this tag too soon. If you can fix this issue, edit the page! |
This comic is the third consecutive comic with solar eclipse as the subject, all three published in the week before the solar eclipse occurring the Monday after, August 21, 2017 which is a total solar eclipse and visible in totality within a band across the contiguous United States from west to east. The other comics are 1876: Eclipse Searches and 1877: Eclipse Science.
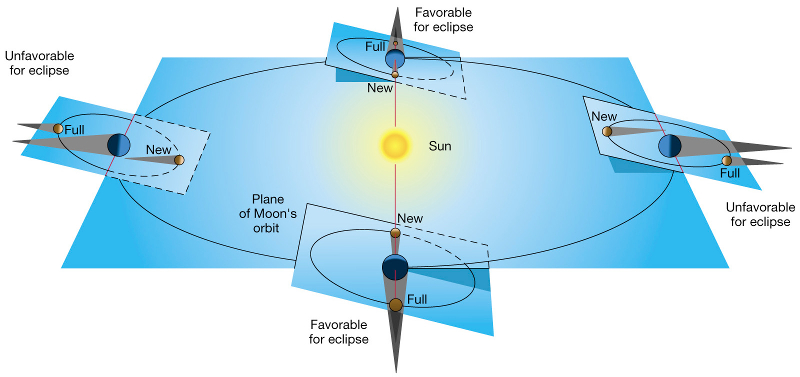
The comic claims that the reason that eclipses don't happen every month is simple to understand by looking at an orbital diagram. Ironically, the cartoon has so many parts and labels that it is far more difficult to understand than is implied. While the graph itself is based on astronomical definitions all the labels are nonsense in this context.
All these labels are complicated words, some are somewhat related to orbital mechanics ("equinox", "perihelion") while some are just Latin-sounding nouns. Moreover, many of the labels provided are kludged, obfuscated, or simply made up. Compare/contrast with the standard Kepler Orbit diagram. Most easily recognizable are the "Dimples of Venus," referring to axis-intersection points in the diagram on Earth.
The title text refers to 'orbit' also being the anatomical term for the eye socket.
All the labels and their astronomical meanings in detail:
- Arctangent
- Arctangent is the inverse function of the tangent function of trigonometry. You can determine a non-right angle of a right triangle by taking the arctangent of the length of the opposite side divided by the length of the adjacent side.
- The angle shown in the comic has no astronomical meaning.
- Astral plane
- The Astral plane is a plane of existence in various esoteric theories. Also used in fictional fantasy context.
- The picture shows the lunar orbital plane, the plane in which the Moon orbits the Earth, tilted about 5.1 degrees from the ecliptic.
- Declension
- Declension is the inflection of nouns in a language.
- In astronomy the declination| is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system. It is measured north or south of the celestial equator, like the geographical latitude on Earth.
- Dimples of Venus
- The Dimples of Venus are indentations sometimes visible on the human lower back.
- In astronomy the Belt of Venus is a shadow cast by the Earth visible in its atmosphere.
- Enceliopsis
- Enceliopsis are small genus of flowering plants in the daisy family, appropriately known as "sunrays".
- In astronomy this point has also no specific meaning. But Enceladus is a moon around Saturn.
- Equinox / Solstice
Equinox and Solstice have a much different meaning:
- Equinoxes are the two instants in the year when the Sun is exactly over the equator; the length of day and night are very nearly equal that day, and it is the first day of spring or the first day of autumn.
- Solstices are the instants in the year when the sun's angle is maximally far from Earth's equator; when one occurs, the length of the day or night is shortest or longest (depending on whether one is in the northern or southern hemisphere), and it marks the first day of summer or winter.
Both types occur because the Earth's rotation axis is tilted (at 23.4 degrees) from its orbital plane (ecliptic) about the Sun.
| Word used in the comics | Meaning of word used | Actual astronomical term | Meaning of actual term |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothecate | A legal verb that means something similar to "make a mortgage" | Hypotenuse | The longest side of a right triangle, opposite the right angle
|
| Obsequity | The state of being obsequious (showing a willingness to obey or serve) | Obliquity | Axial tilt |
| Perihelix | Portmanteau of helix and perihelion | Perihelion | The point in a solar orbit that is closest to the Sun |
| Prolapse | A medical condition in which an internal organ is slipped forward or down |
| |
| Sagittal plane | Anatomical plane, dividing the body in left and right | Ecliptic plane and Sagittarius | The plane of the Earth's orbit about the Sun, and a constellation in the Zodiac
|
| Solar plexus | Network of nerves located in the abdomen. | Solar | An adjective referring to the Sun, the star in our solar system.
|
| Tropopause | The boundary in our atmosphere between the troposphere and stratosphere, defined as the boundary where air ceases to cool with increasing elevation. It is 9-17 km above sea level, not the thousands of kilometers as depicted here. |
Explanation for "Why isn't there a (solar) eclipse every month?"
If the plane of where the Earth orbits the Sun and where the Moon orbits the Earth were completely aligned, then there would be a solar eclipse at every new moon (once every 29.5 days) and a lunar eclipse at every full moon (half a lunar period about 14.7 days after a New Moon). However, the plane in which the Moon orbits the Earth is tilted with an inclination of 5 degrees relative to that of the ecliptic plane (the plane defined by the Earth's orbit around the Sun). Eclipses are only possible during two eclipse seasons each year (half a year apart) where for a period of 31 to 37 days the Sun is nearly aligned with the two points in the tilted Earth-Moon plane where the Moon crosses the ecliptic plane. During an eclipse season at the time of a new moon there will be solar eclipses visible from certain locations and during full moons there will be lunar eclipses.
The real explanation of eclipses is evident from this xkcd comic, but is labeled with a fictional character similar to a Greek phi but with two vertical lines; the remaining labels also do not contribute to this explanation and exist only to distract or misinform the reader.
Transcript
| This is one of 40 incomplete transcripts: Do NOT delete this tag too soon. If you can fix this issue, edit the page! |
- [An orbital map of the Earth is shown. The Sun is in the center, the Earth is at the right bottom, and the Moon is left below the Earth.]
- Why isn't there an eclipse every month?
- This is a common question! The answer is made clear by a quick look at the Earth's orbital diagram:
- [Label Sun:]
- Solar plexus
- [Label on the Earth's plane:]
- Sagittal plane
- [Labels on Earth's orbit (beginning at the Earth counterclockwise):]
- Perihelix, Declension, Obsequity, Hypothecate, Enceliopsis, Equinox (Solstice in British English)
- [Two angles in the plane are labeled as:]
- Determinant of the date of Easter, Arctangent
- [The plane of the Moon is pictured in a small angle to the Earth's plane and named Astral Plane. The angle is presented between two lines (Greek Nu or Gamma and a double Greek Chi) and identified by a character that looks similar to a Greek Phi but with two vertical lines.]
- [The labels at the Moon's path are:]
- Tropopause, Prolapse, Errata.
- [An arrow points to the Earth at the zero meridian on the equator. The label reads:]
- Dimples of Venus
Discussion
I guess first off, we should note the "solstice" is *not* the Bristish equivalent of "equinox" -- they are actually opposites. The equinoxes occur in April and September, when the day & night are equal length, and the solstices occur in June and December, when the length of daylight and nightime, respectively, are at their longest. JamesCurran (talk) 15:30, 18 August 2017 (UTC)
- Technically, the opposite of solstice is the other solstice. Solstice and equinoxes are orthogonal. -- Hkmaly (talk) 00:01, 20 August 2017 (UTC)
Being picky but the Equinox/Solstice section refers to equinoxes marking the start of either spring or autumn, but actually both equinoxes mark the beginning of both spring and autumn in opposite hemispheres. ExternalMonolog (talk) 22:08, 22 August 2017 (UTC)
"Determinant of the date of Easter" refers to the fact that in the Catholic Church (and possibly other Christian denomiations) the date of Easter is the first Sunday after the first full moon of Spring, which means it is an astronomical calculation, but completely unrelated to the indicated angle. JamesCurran (talk) 16:28, 18 August 2017 (UTC)
- Well, everyone celebrates Easter on the same day, right? So it's the first Sunday after the first full moon for everybody. Berets (talk) 23:20, 18 August 2017 (UTC)
- No, not all denominations agree on the date of Easter; a particular example being the Orthodox church, which usually has Easter a week after the Catholic church, but sometimes as much as five weeks later. The difference is caused by the two denominations using different idealized calendars, both lunar and solar, as well as a slight difference in the definition. 162.158.69.57 18:41, 19 August 2017 (UTC)
"Astral planes" might as well be a Unicode reference, taking into account Randall's occasional mention of emoji, since emoji reside on one of the astral planes: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plane_%28Unicode%29 141.101.105.168 (talk) (please sign your comments with ~~~~)
- That supplementary planes humorously refer also to Astral planes as mentioned in this explanation.--Dgbrt (talk) 19:54, 18 August 2017 (UTC)
Solstice comes from the Latin ... Sol = Sun .. Sistere = Stand still. It literally means the day the sun stands still and refers to the longest day of the year (summer) and the shortest day of the year (winter). So how does the Sun "stand still". On those days the Earth reaches either end of orbital ellipse and returns around the other side. If you stick a pole in the ground and observe its shadow every day at Noon you will see the shadow grow longer every day from winter to summer and grow shorter every day from summer to winter. The shadow is shortest when the Sun is highest in the sky at mid-summer and the shadow is longest when the sun is lowest in the sky at mid-winter. The sun is either getting higher in the sky or lower in the sky every day. When the Earth is at the end of the ellipse and the transition takes place the shadow will not make any noticeable change from one day to the next and one could say that the "Sun has stood still". Rtanenbaum (talk) 19:36, 18 August 2017 (UTC)
I think that Solstice/Equinox thing is a reference to Randall having a hobby of spreading linguistic misinformation, as seen in 1677:Contrails. 172.68.26.251 00:32, 19 August 2017 (UTC)
I'm not sure what the labels of the planes are, but they certainly aren't Greek letters. They look like alchemical symbols to me. 162.158.74.243 00:56, 20 August 2017 (UTC)
Part of the humor of Declension is that it's a portmanteau of right ascension and declination. Right now only declination is mentioned. 162.158.75.40 02:43, 20 August 2017 (UTC)
Arctangent is also a music festival in the UK, happening when this comic came out. --162.158.234.46 22:30, 21 August 2017 (UTC)
Enceliopsis could use a little more detail, as there's a funny little redundancy there. The "-psis" suffix refers to the apex of an orbit, i.e., the apoapsis is the farthest orbit point and the periapsis is the closest. And the "-helion" suffix in aphelion/perihelion is the same thing, but for the more specific case of orbits around the sun. So using both together in the case of "-elio-psis" effectively gives a suffix with the meaning "pertaining to an orbital apex and pertaining to an orbital apex around the sun".
SomeDee (talk) 14:54, 22 June 2023 (UTC)